Index
Get the latest news right in your inbox
In today's fast-paced digital universe, a technology is emerging that is as fascinating as it is alarming: deepfake. This term, which merges "deep learning" and "fake", defines multimedia content - videos, audios and images - manipulated by Artificial Intelligence to create hyper-realistic and virtually undetectable fakes. What started as an experiment in forums has become one of the most sophisticated phishing tools and a global cybersecurity challenge.
Understanding what a deepfake is and how it works is not just a matter of technological curiosity; it is a necessity to protect our identity, the reputation of our companies and the integrity of our digital processes. From million-dollar frauds to the manipulation of public opinion, the impact of deepfakes is already a tangible reality. Here we will take an in-depth look at this technology, working process, the risks to users and businesses, and how to combat it effectively with advanced AI and biometrics tools.
What is a Deepfake: Anatomy of a Digital Hoax
A deepfake is, in essence, a synthetic digital artifact. Unlike a simple video edit or Photoshop montage, a deepfake is not edited manually. It is generated. Using learning algorithms, an AI system analyzes huge amounts of data from a real person (images, videos, voice recordings) to learn how to mimic their appearance, gestures, expressions and voice accurately.
The result is video or audio that looks completely authentic, where a person appears to say or do things they never did. The underlying technology, known as deepfake AI, can superimpose one person's face on another's body, animate a photograph or clone a voice from a sample of just a few seconds.
This level of realism makes deepfakes the perfect vehicle for misinformation, fraud such as identity theft and cybercrime.
Types and Examples of Deepfakes
It manifests itself in various forms,with their own applications and levels of sophistication. The most common types are:
- Face Swap: This is the most well-known application. Replacing the face of one person in a video or image with that of another. Initial, and often viral, examples involve celebrities, such as the video where actor Steve Buscemi's face is superimposed on Jennifer Lawrence's face. Although they may seem trivial, these techniques are the basis for more complex identity fraud.
- Lip Sync: An algorithm manipulates lip movements in a video to synchronize with different audio. This makes it possible to create videos in which a public figure, such as a politician or CEO, appears to deliver a speech they never gave. One example was the deepfake of Binance's CEO, who had to deny a manipulated video showing him promoting a project.
- Voice Cloning: Uses deepfake AI to synthesize a person's voice from an audio sample. More advanced systems can clone a voice with a high degree of fidelity, mimicking pitch, cadence and intonation. This technique is the cornerstone of vishing (voice phishing) scams. In 2024, an employee of a multinational company in Hong Kong was tricked into transferring $25 million after participating in a video conference with deepfake recreations of several of his company's executives.
- Full Body Puppetry: This is one of the most advanced forms. Here, the AI not only manipulates the face, but animates a person's body movements to mimic those of another. This makes it possible to create hyper-realistic avatars or to completely control a person's appearance in a video.
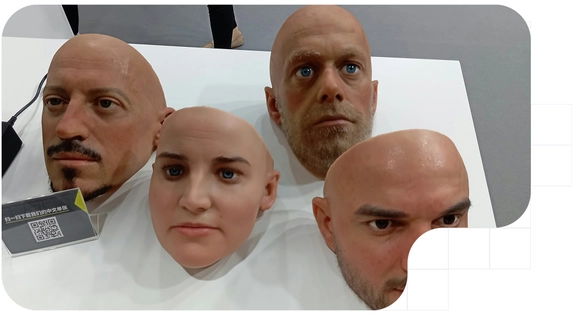
Differences From Other Impersonation Tools
It is crucial to distinguish deepfakes from other, simpler forms of digital manipulation, often referred to as "cheap fakes."
The fundamental difference between a deepfake and cheap fake lies in their origin and realism. While deepfakes are automatically generated by AI that learns to create smooth, hyper-realistic fakes, cheap fakes are the result of manual editing with conventional software (such as Photoshop), so they often have inconsistencies and visual artifacts that make them easier to detect with the naked eye.
Current Uses of Deepfakes: How They are Affecting Users and Businesses
There are positive applications in industries such as film (actor rejuvenation) or education, but the malicious use of deepfakes dominates public debate due to their devastating potential. The main battleground is fraud and security in digital onboarding processes.
Companies, in their attempt to digitize and streamline customer acquisition, have implemented remote onboarding processes. These processes require identity verification ( known as KYC - Know Your Customer) to comply with regulation and avoid fraud. This involved showing an identity document to a camera and performing a proof of life, such as smiling or shaking your head.
This is where deepfakes have blown up the game board. Cybercriminals no longer need physical masks or actors. Using a deepfake app available on the web and a victim's photo stolen from their social media, they can generate a short video that passes these basic life tests. They can animate the photo to blink, smile or shake their head, fooling unsophisticated identity verification systems.
This type of attack, known as an injection attack, has catastrophic consequences:
For Businesses:
- Increased Fraud: It allows the opening of bank accounts, the application for credit or contracting services in the name of victims, generating direct financial losses and an increase in delinquency rates.
- Legal and Compliance Impact: An onboarding process vulnerable to deepfake fraud breaches key regulations such as Anti Money Laundering (AML). The fines for non-compliance are in the millions and reputational damage can be irreparable.
- Trust and Sales Erosion: If customers perceive that a platform is not secure, trust plummets. Not only does this affect retention, it also slows new user acquisition, directly impacting growth and sales. Implementing stricter security measures can generate user friction and frustration, leading to abandonment.
For Users:
- Identity Theft: The victim sees their identity used to commit crimes, which can lead to legal problems, and an arduous process to clear their record.
- Financial Loss and Blackmail: Criminals may use the stolen identity to drain the victim's accounts, to extort money or threaten to post fake compromising videos.
- Psychological and Reputational Damage: Being a victim of a deepfake can cause significant stress and distress, as well as lasting personal and professional reputational damage.
Deepfakes and AI, How Will They Evolve?
The evolution of deepfakes is intrinsically linked to the advancement of Artificial Intelligence. We are in a technological arms race: as detection tools are developed, deepfake generation algorithms become more sophisticated to circumvent them.
The trends that will shape the future are clear:
- Real-Time Deepfakes: The ability to generate and overlay deepfakes during a video conference or live broadcast is no longer science fiction. This raises the risk of fraud to a new level.
- Reduced Need for Data: Where early deepfakes required thousands of images of the victim, the new models can generate credible fakes from a single image or audio clip.
- Multi-Modal Hyperrealism: Future deepfakes will not only mimic face and voice, but will replicate breathing patterns, nervous tics and other subtle biometric cues, making manual detection virtually impossible.
- Expansion into New Domains: We will see deepfakes applied not only to humans, but to the creation of fake identity documents, the alteration of satellite images or the manipulation of digital forensic evidence.

Technical Functioning of Deepfakes
To understand how to combat deepfakes, it is essential to understand their technical architecture. The core technology behind most deepfakes is Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs).
A GAN consists of two neural networks competing against each other in a zero-sum game:
- The Generator: Its mission is to create the fakes. It is fed random noise and its goal is to produce an image, video, or audio that is indistinguishable from the real thing. At first, his creations are crude and chaotic.
- The Discriminator: Acts as a detective or critic. His job is to receive both real images (from training data) and the fake images created by the Generator, and decide which are authentic and which are not.
The training process is a constant feedback loop:
- The Generator creates a batch of fake images and sends them to the Discriminator.
- The Discriminator evaluates and provides feedback: "this is fake", "this looks real".
- This feedback is used to adjust the parameters of the Generator, which learns from its mistakes and tries to create a better fake on the next attempt.
- At the same time, the Discriminator also learns. As it sees more examples, both real and fake, it becomes increasingly skilled.
This antagonistic "duel" is repeated millions of times. The Generator becomes an increasingly skilled forger, and the Discriminator becomes an increasingly sharp detective. The cycle continues until the Generator produces fakes so perfect that the Discriminator can no longer distinguish them from the real thing. At that point, the deepfake is ready.
Another common architecture is autoencoders, which are used for face swaps. An autoencoder is trained to compress an image into a low-dimensional latent representation (the "essence" of the face) and then reconstruct it. By training one autoencoder with thousands of images of Person A and another with images of Person B, the "decoders" can be swapped to reconstruct Person A's face with Person B's facial attributes.
How to Identify a Deepfake: Detect it with AI and KYC APPs
Although deepfakes are becoming more and more perfect, there are still red flags. Manual detection, although increasingly unreliable, can be fixed by:
- Anomalous Blinking and Eye Movement: Early AI models often did not replicate the natural frequency of blinking.
- Inconsistencies in Lighting and Shadows: Especially at the edges of the overlapping face.
- Digital Artifacts: Blurred or pixelated areas.
- Unnatural Facial Expressions: A smile that does not affect the eyes or a lack of emotion that does not match the tone of voice.
- Imperfect Lip Sync.
However, relying on the human eye is a losing strategy. The real defense lies in detection by AI, which can analyze aspects imperceptible to us. These systems look for digital fingerprints, inconsistencies in pixel flow, camera noise patterns or subtle biological signals that give away the counterfeit.
This is where advanced KYC solutions make a difference. They are robust identity verification systems designed for the business environment. As is Tecalis Identity, a platform that integrates multiple anti-deepfake controls directly into the verification flow, invisibly to the user.
Tecalis Identity controls go beyond asking for a smile, implementing a defense in depth that includes:
- Passive and Active Liveness Detection: Analyzes real-time video for micro-expressions, eye glints and skin texture changes that only a human being in front of the camera can produce.
- 3D Depth Analysis: Using light and shadow analysis, the system creates a 3D map of the face to ensure that it is not a flat image or a video projected on a screen.
- Injection Attack Detection: The platform is able to identify if the camera source has been tampered with or if a pre-recorded video is being injected by deepfake AI.
- Behavioral Analysis: The system monitors suspicious patterns in hardware, network and user behavior during the process, alerting to any anomalies.
These sophisticated anti-deepfake controls are also integrated into e-signature solutions such as Tecalis Sign. By requiring robust biometric identity verification before a contract can be signed, it ensures the highest level of security that the person signing is who they say they are. The result is a smooth and frictionless contracting flow.
Digital Tools for Companies: Avoiding Deepfake Fraud with KYC and Biometrics
For a company, integrating a robust defense against deepfakes is not an option, it is a strategic necessity. Solutions such as Tecalis are offered as a service (IDaaS - Identity as a Service) that is easily and quickly integrated into any application or enterprise web via an API (Application Programming Interface).
This API integration allows a bank, insurance company or telecommunications company to add a highly secure identity verification process in a matter of days.
- API Invocation: When a new customer initiates a registration process on the company's website or app, the company's system makes an API call to the identity verification platform.
- Secure Evidence Capture: The Tecalis solution securely takes control. OCR technology (Optical Character Recognition) automatically extracts the data.
- Biometric Verification and Proof of Life: The user records a short video of his face. During this recording, the AI runs in the background: passive liveness analysis, 3D depth detection, texture analysis, etc. It compares the face in the video with the ID photo.
- Anti-Fraud Analysis: Algorithms analyze the video for any signs of tampering, deepfake, or attack.
- Response and Verification: In a matter of seconds, the platform completes more than 20 security checks and returns a response to the enterprise via API: identity verified or fraud alert.
This multi-layered approach, combining document verification, facial biometrics and active/passive liveness detection with AI, creates an ecosystem of digital trust. It not only shields the enterprise against deepfake fraud, but also ensures compliance with stringent regulations (such as eIDAS), optimizes the customer experience by providing a fast and frictionless process. The threat of deepfakes is constantly evolving, but with the right tools, we can stay one step ahead, protecting our identity.