Index
Get the latest news right in your inbox
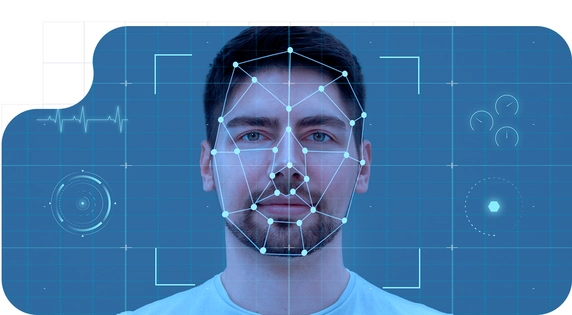
Biometric control has established itself as an essential pillar of modern security, both in physical and digital environments. Based on unique and non-transferable features, it overcomes the limitations of passwords, cards, or PIN codes. This technology ensures more accurate, fraud-resistant, and highly efficient identification.
In a context marked by the rise of cybercrime, identity theft, and unauthorized access, biometric systems offer a robust and scalable solution. They are widely adopted in digital banking, corporate buildings, mobile applications, and digital identity systems. In addition, they comply with current data protection standards and security regulations.
This article analyzes what biometric control is, its types, applications, and advantages, as well as Tecalis' solutions for secure identity and access management.
What is biometric control and how does it work?
Biometric control is a security system that allows a person to be identified or authenticated based on unique, measurable, and verifiable biometric characteristics. These characteristics can be physical, physiological, or behavioral, and have the particularity of being extremely difficult to falsify, share, or steal.
In practical terms, a biometric access control system works through the following phases:
- Biometric data capture: The system collects the biometric characteristic using a specialized sensor (fingerprint reader, facial camera, iris scanner, microphone, etc.).
- Processing and feature extraction: The captured data is converted into a mathematical biometric template using advanced algorithms.
- Secure storage: The template is stored in encrypted form in a secure database, in compliance with legal and technical requirements.
- Comparison and identity verification: When the user attempts to access, the system compares the biometrics presented with the stored template.
- Access decision: If the level of match exceeds a defined threshold, access is granted; otherwise, it is denied.
This process can be completed in milliseconds, making biometric control a fast, convenient, and highly reliable system.
Difference between biometric identification and authentication
In biometrics, it is essential to distinguish between identification and authentication, two concepts that are often confused but have very different technical and security implications.
Biometric identification (1:N)
The system compares the captured biometrics with all the stored templates to determine who the person is. It answers the question: "Who is this user?" It is common in mass access control, surveillance, or border control.
Biometric authentication (1:1)
The user claims to be someone (for example, by entering a username or ID) and the system verifies whether their biometrics match the associated template. It answers the question: "Are you really who you say you are?" It is the most widely used method in corporate and digital biometric access control.
Biometric authentication is faster, more accurate, and more common in corporate environments and online applications.

Why is biometric control important in security and access?
The importance of biometric control lies in its ability to solve the main security problems associated with traditional access methods.
Passwords are forgotten, reused, and stolen. Cards are lost, duplicated, or lent to others. PINs can be observed or shared. Biometrics, on the other hand, are inherent to the individual and cannot be forgotten or transferred.
Biometric security: prevention of fraud and unauthorized access
One of the biggest problems with traditional authentication systems is their vulnerability to identity fraud. Biometric security is one of the most effective tools against:
- Identity theft.
- Credential theft.
- Internal fraud.
- Unauthorized access.
- Phishing attacks.
- Misuse of corporate accounts.
By relying on unique characteristics, biometric systems drastically reduce the risk of one person gaining access using another person's credentials.
In addition, modern systems incorporate liveness detection, which prevents attacks using photos, videos, masks, or voice recordings, further increasing the level of security.
Biometric access control in companies and organizations
In the corporate environment, biometric access control is key to protecting:
- Buildings and offices: prevents unauthorized access and replaces easily duplicated physical credentials.
- Restricted or high-security areas: ensures that only authorized and validated personnel can access sensitive areas.
- Data centers and server rooms: protects critical infrastructure from intrusion and sabotage.
- Laboratories and critical facilities: ensures the integrity of processes, information, and strategic assets.
- Internal computer systems: strengthens user authentication and reduces the risk of credential theft.
- Digital platforms and online tools: prevents fraudulent access and improves the security of the corporate digital environment.
- Manufacturing and logistics: control access to production processes and operational areas, improving traceability and security.
Companies use biometric systems to ensure that only authorized personnel can access certain spaces or systems, creating complete traceability of accesses and events.
In the digital realm, biometrics is integrated with:
- Corporate applications: enables secure and agile authentication for employees and collaborators.
- VPN and remote access: reinforces secure access to the corporate network from external locations.
- Business software (ERP, CRM): protects sensitive information and critical business transactions.
- Cloud platforms: adds an additional layer of security in shared and scalable environments.
- Digital identity systems: facilitates reliable user verification and unified identity management.
This enables strong, frictionless authentication aligned with Zero Trust Security models.
Advantages over other access control systems
Biometric access control systems offer clear advantages over traditional methods:
- Greater security: drastically reduces fraud and impersonation.
- Accuracy: minimal error rates thanks to advanced algorithms.
- Speed: authentication in seconds or milliseconds.
- Convenience: eliminates the need to remember passwords or carry cards.
- Traceability: detailed record of accesses and events.
- Cost reduction: less management of physical credentials.
- Scalability: easy integration into existing systems.
For these reasons, biometrics is considered one of the most reliable methods of modern authentication.
Most commonly used types of biometric systems
There are various types of biometric systems, each with specific characteristics depending on the level of security required and the context of use:
- Facial recognition: Analyzes facial features using cameras and computer vision algorithms. Widely used in physical access and mobile applications. Ideal for healthcare or high-traffic environments.
- Fingerprint: One of the most widely used systems. High accuracy and low implementation cost. Commonly used in mobile devices, physical access systems, and time clocks.
- Iris and retina recognition: Extremely accurate. Used in high-security environments.
- Voice biometrics: Analyzes unique vocal patterns. Common in call centers and telephone systems.
- Behavioral biometrics: Evaluates patterns such as how a person writes, moves, or interacts with a device.
- Biometric signature: Analyzes the dynamics and pressure of a digital handwritten signature.
Each system can be used independently or in combination within multi-factor authentication (MFA) schemes.
Main applications: Where is biometric control used?
Biometric control has applications in both physical and digital environments. Its use has expanded to multiple sectors:
Physical biometric access control
- Companies and offices.
- Corporate buildings.
- Airports and transportation.
- Hospitals and healthcare centers.
- Public institutions.
Biometric security in devices and applications
- Smartphones and tablets.
- Banking applications.
- Fintech platforms.
- E-commerce.
- Corporate software.
Digital identity and business processes
- Electronic signature.
- Remote identity verification.
- Fraud prevention.
Biometrics is now a central element of secure digital transformation.
Legal framework and data protection in biometrics
Biometric data is considered special category personal data under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and similar laws in other countries (LOPDGDD in Spain).
Key legal points of the GDPR (Art. 9):
- Explicit and informed consent to process biometric data.
- Clear legal basis for processing.
- Application of the principle of data minimization and encryption.
- Data must be stored in an encrypted and decentralized manner.
- Enhanced technical and organizational measures.
European guidelines (EDPB):
- They prohibit the mass and non-selective use of biometrics in public spaces without an impact assessment.
- They require data protection impact assessments (DPIAs) for biometric systems in companies.
- Recommend the use of irreversible templates and privacy-by-design technologies.
Organizations must ensure that biometric systems comply with the principles of privacy by design and by default.
Minimum security requirements for biometric systems
A secure biometric control system must comply with at least the following:
- Strong end-to-end encryption of biometric data: ensures confidentiality and integrity both in transit and at rest.
- Secure storage of templates (not images): reduces the risk of exposure by using secure elements such as Secure Enclave, TPM, or HSM.
- Liveness detection: mitigates impersonation through active or passive verification of the real user.
- Auditing and traceability: allows access and security events to be logged, monitored, and reviewed.
- MFA integration: adds additional layers of authentication to reduce the risk of compromise.
- Identity and access management (IAM): centrally control permissions, roles, and user lifecycles.
- Protection against replay attacks: use of unique tokens per session.
- Regulatory compliance: ensures alignment with applicable data protection and privacy regulations.
Security does not depend solely on the sensor, but on the entire system architecture.
Tecalis solutions for biometric control and access security
Tecalis offers advanced biometric control, digital identity, and access security solutions tailored to demanding business and digital environments. A comprehensive portfolio that covers all biometric access control and identity verification needs:
Tecalis Identity
Tecalis Identity is a digital identity management platform with biometric verification, remote onboarding, and advanced authentication. The solution includes an identity management platform with support for 1:1 biometric authentication. It is compatible with WebAuthn and FIDO2 standards, enabling passwordless login in both browsers and applications.
It also supports integration with multiple biometric modalities, including fingerprint, facial recognition, and voice recognition.
Tecalis Sign
Tecalis Sign is an advanced and qualified electronic signature solution that, at its highest level, can integrate a biometric seal. This provides maximum legal evidence, irrevocably linking the signature on the document to the verified biometric identity of the person, guaranteeing non-repudiation.
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) and Single Sign-On (SSO) Module
Tecalis allows you to strengthen access to corporate applications by implementing biometric authentication as a possession/inherence factor within an MFA scheme (e.g., "something you know" - password + "something you are" - fingerprint). Its ability to integrate with standards such as SAML or OAuth facilitates the implementation of SSO, allowing users to access multiple applications with a single strong biometric authentication.
Anti-fraud and document verification solutions
Beyond access control, the Tecalis platform incorporates advanced intelligence to detect fraudulent patterns during identity verification, such as document manipulation, the use of virtual devices, or sophisticated impersonation attempts.